Microfluidic models of hemostasis and thrombosis
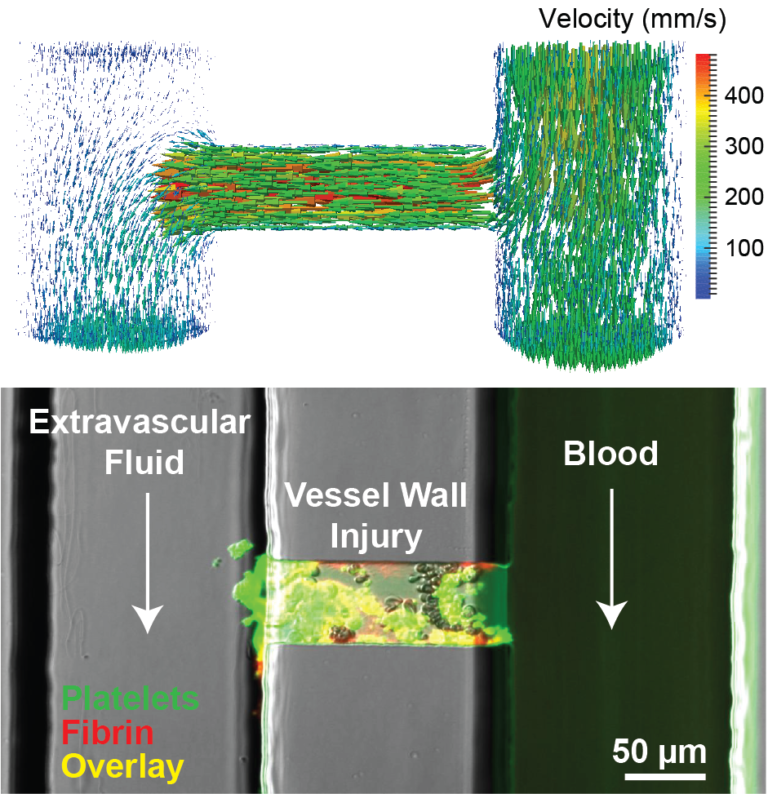
Blood flow is a central regulator of blood clot formation; it transports blood cells and proteins to and from a clot and imposes forces that mediate cell adhesion and aggregation. We have developed a series of models for measuring and modeling different types clotting events including bleeding, deep vein thrombosis, and arterial thrombosis. We use microfluidic techniques in combination with optical microscopy to measure clot formation as as function of forces, geometry, and initiators and inhibitors of platelet function and coagulation. These models have been used to reveal fundamental mechanisms regulated by forces and flows and as tools to diagnose and measure the efficacy of therapies for bleeding and thrombotic disorders.
Related Publications
P. Mangin, K.B. Neeves, W.A. Lam, J.M.E.M Cosemans, N. Korin, S.W. Kerrigan, M. Panteleev. In vitro flow-based assay: from simple towards more sophisticated models for mimicking hemostasis and thrombosis. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 19 (2021):582-587. DOI: 10.1111/jth.15143
M.G. Sorrells, K.B. Neeves. Adsorption and absorption of collagen peptides to polydimethylsiloxane and its influence on platelet adhesion flow assays. Micromachines, 11 (2020): 62. DOI: 10.3390/mi11010062
M. Lehmann, R.M. Schoeman, P.J. Krohl, A.M. Wallbank, J.R. Samaniuk, M. Jandrot-Perrus, K.B. Neeves. Platelets drive thrombus growth in a hematocrit and glycoprotein VI dependent manner in an in vitro model of venous thrombosis. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 38 (2018): 1052-1062. DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.310731.
R.M. Schoeman, M. Lehmann, K.B. Neeves. Flow chamber and microfluidic approaches for measuring thrombus formation in genetic bleeding disorders. Platelets, 28 (2017): 463-471. DOI: 10.1080/09537104.2017.1306042.
O.J.T. McCarty, D. Ku, M. Sugimoto, M.R. King, J. Cosemans, K.B. Neeves. Dimensional analysis and scaling relevant to flow models of thrombus formation. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 14 (2016): 619-622. DOI: 10.1111/jth.13241
S. Zhu, B.A. Herbig, R. Li, T.V. Colace, R.W. Muthard, K.B. Neeves, S.L. Diamond. In microfluidico: Recreating in vivo hemodynamics using miniaturized devices. Biorheology, 52 (2015): 303-318. DOI: 10.3233/BIR-15065.
B.R. Branchford, C.J. Ng, K.B. Neeves, J.A. Di Paola. Microfluidic technology as an emerging clinical tool to evaluate thrombosis and hemostasis. Thrombosis Research, 136 (2015): 13-19. DOI: 10.1016/j.thromres.2015.05.012.
K.B. Neeves, S.F. Maloney, K.P. Fong, A.A. Schmaier, M.L. Kahn, L.F. Brass, and S. L. Diamond. Microfluidic focal thrombosis model for measuring murine platelet deposition and stability: PAR4 signaling enhances shear-resistance of platelet aggregates. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 6 (2008), 2193-2201. DOI: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2008.03188.x